
Back ارتباط (إحصاء) Arabic সহ-সম্বন্ধ Assamese Correlación AST Korrelyasiya Azerbaijani Карэляцыя Byelorussian Карэляцыя BE-X-OLD Корелация Bulgarian সংশ্লেষ ও নির্ভরশীলতা Bengali/Bangla Koeficijent korelacije BS Correlació Catalan
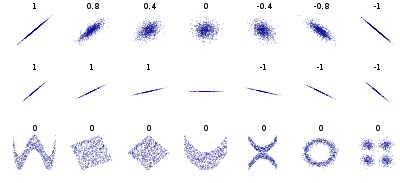
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are linearly related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the so-called demand curve.
Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. However, in general, the presence of a correlation is not sufficient to infer the presence of a causal relationship (i.e., correlation does not imply causation).
Formally, random variables are dependent if they do not satisfy a mathematical property of probabilistic independence. In informal parlance, correlation is synonymous with dependence. However, when used in a technical sense, correlation refers to any of several specific types of mathematical relationship between the conditional expectation of one variable given the other is not constant as the conditioning variable changes; broadly correlation in this specific sense is used when is related to in some manner (such as linearly, monotonically, or perhaps according to some particular functional form such as logarithmic). Essentially, correlation is the measure of how two or more variables are related to one another. There are several correlation coefficients, often denoted or , measuring the degree of correlation. The most common of these is the Pearson correlation coefficient, which is sensitive only to a linear relationship between two variables (which may be present even when one variable is a nonlinear function of the other). Other correlation coefficients – such as Spearman's rank correlation – have been developed to be more robust than Pearson's, that is, more sensitive to nonlinear relationships.[1][2][3] Mutual information can also be applied to measure dependence between two variables.
- ^ Croxton, Frederick Emory; Cowden, Dudley Johnstone; Klein, Sidney (1968) Applied General Statistics, Pitman. ISBN 9780273403159 (page 625)
- ^ Dietrich, Cornelius Frank (1991) Uncertainty, Calibration and Probability: The Statistics of Scientific and Industrial Measurement 2nd Edition, A. Higler. ISBN 9780750300605 (Page 331)
- ^ Aitken, Alexander Craig (1957) Statistical Mathematics 8th Edition. Oliver & Boyd. ISBN 9780050013007 (Page 95)
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search



